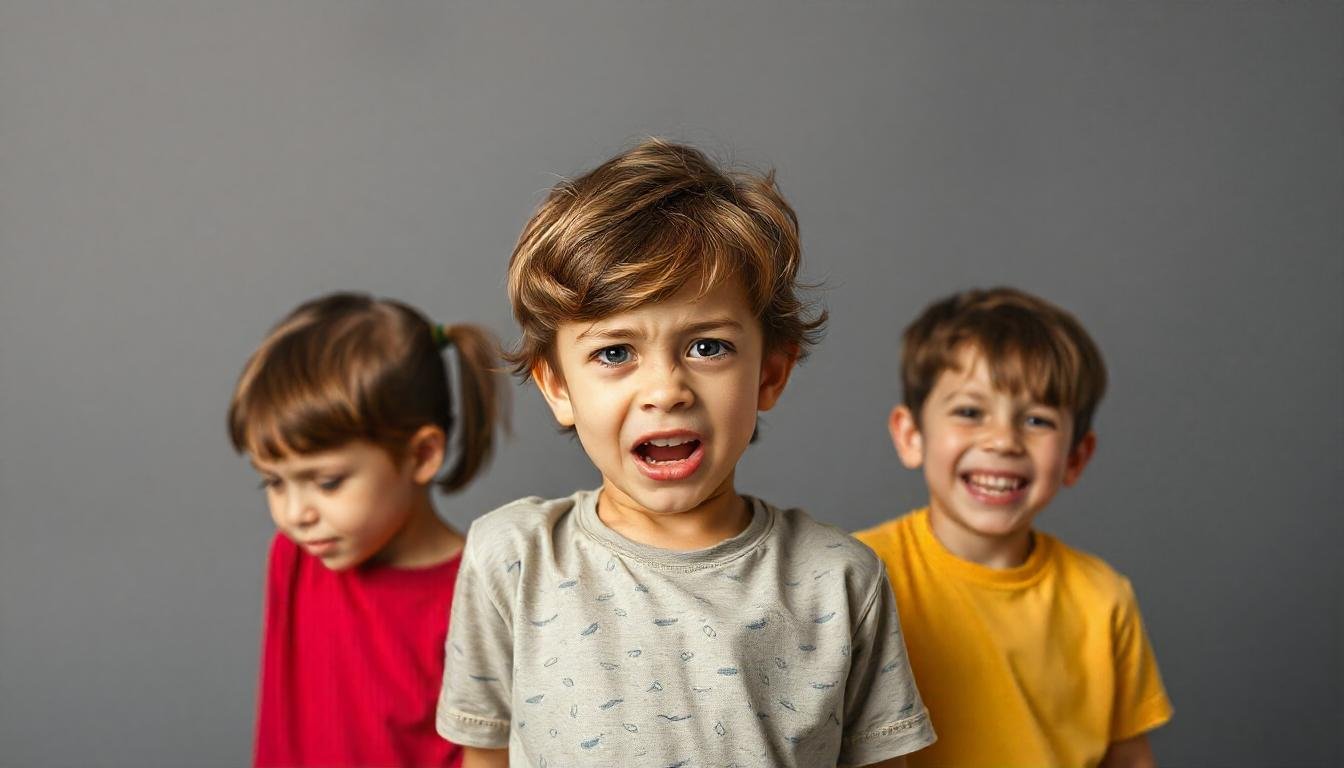

What is ADHD?
Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder commonly diagnosed in children but often continues into adulthood. It is characterized by symptoms such as inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity, which can impact academic performance, social interactions, and daily functioning. Understanding ADHD Treatment is crucial for effective management and support for those affected.
Please keep in mind that therapy and medication are the most effective ways to treat ADHD.
Possible Causes of ADHD
While the exact causes of ADHD are not fully understood, research indicates several potential factors. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), genetic predisposition plays a significant role, with ADHD often running in families. Other contributing factors may include:
- Brain Structure and Function: Differences in brain anatomy and neurotransmitter levels have been observed in individuals with ADHD.
- Environmental Influences: Exposure to toxins, particularly during pregnancy, such as alcohol and tobacco smoke, may increase the risk of developing ADHD.
- Premature Birth and Low Birth Weight: These factors have been linked to a higher likelihood of ADHD diagnosis.
Sources like the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) and the CDC provide valuable insights into these potential causes, emphasizing the multifaceted nature of ADHD.
Non-Medication Treatments
ADHD treatment without medications may be possible in some cases. The National Institutes of Health (NIH) and the Mayo Clinic have highlighted some effective strategies. Some of these are as follows:
- Behavioral Therapy: This involves working with a therapist to develop coping strategies and improve behavior. Parents and children can learn techniques to manage symptoms and improve communication.
- Parent Training: Educating parents on effective strategies for managing their child’s behavior can lead to better outcomes. This training can help parents reinforce positive behaviors and provide consistent consequences for negative ones.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): This type of therapy helps individuals with ADHD develop problem-solving skills and address negative thinking patterns.
- Sound sleep: Get plenty of sleep without any disturbance. Try to switch off your phone and any screens at least 1 hour before your sleeping time.
- Consistency: Maintain a consistent routine. This includes a specific sleep time as well.
- Exercise and Physical Activity: Regular physical activity can help reduce ADHD symptoms by improving focus, mood, and self-esteem.
- Dietary Modifications: While there’s no specific diet for ADHD, some studies suggest that a balanced diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids may help improve symptoms. Consultation with a healthcare professional can provide tailored dietary advice.
- Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Practices such as mindfulness meditation can help enhance concentration and reduce impulsivity.
- Things to Avoid: Limit your alcohol and tobacco intake.
Treating Children with ADHD
ADHD treatment without medication involves complete care. Children with ADHD should be treated with a special approach, considering their specific needs and challenges. Creating a supportive environment is essential. Strategies include:
- Consistent Routines: Establishing clear routines helps children with ADHD feel secure and understand expectations.
- Positive Reinforcement: Celebrating successes, no matter how small, can boost self-esteem and encourage good behavior.
- Educational Support: Parents’ collaboration with teachers can be effective. As this can lead to some extra support in the classroom. This may improve child’s overall result as well.
The Role of PGx Testing
Getting to know that the medication you are being prescribed will not have any side effects or it will not show any reactions is a relief. Pharmacogenomic PGx testing can play a crucial role in identifying the most effective treatment options for individuals with ADHD. These tests analyze how a person’s genetic makeup affects their response to a specific medication. By tailoring treatment plans based on PGx results, healthcare providers can optimize therapy, minimize side effects, and improve overall treatment efficacy.
Conclusion
ADHD is a complex disorder that requires a comprehensive approach for effective management. While medication and therapies are the most effective in this case, ADHD treatment without medication is also possible. By combining behavioral therapies, lifestyle changes, and some more changes (stated above), patients with ADHD may be treated. If taken care of, Individuals with ADHD can thrive and reach their full potential.
Please note that this blog is intended only for informational purposes. Always consult a doctor before taking any medical action.


Leave a Reply